- +1 800 433 4609
- |
- Request Info
Early detection of
Peripheral Arterial Disease
Next generation non-invasive patient diagnostics within minutes.
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
The ABI is an indicator of Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), a cardiovascular disease with a high mortality rate.
Unfortunately, the ABI is not measured routinely because its traditional measuring with Doppler ultrasound is long and complex.
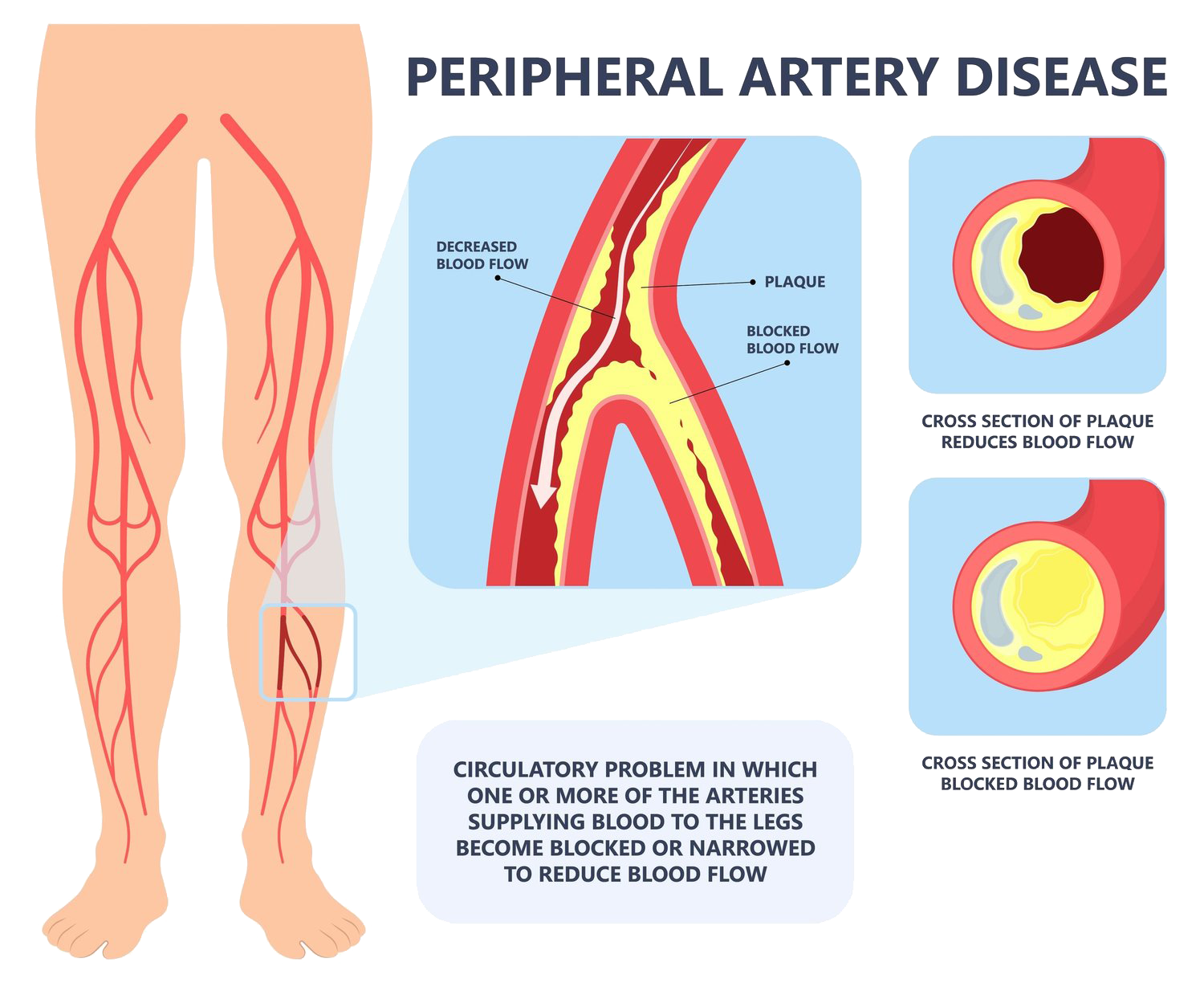
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is highly underdiagnosed.
2 out of 3 patients with PAD do not show signs or symptoms.
The cost to treat individuals with progressive PAD is astronomical.
VitalScan Plus ABI+ solutions enable fast and effective measurement of the Ankle-Brachial Index.
Automated Ankle-Brachial Index system with its 4 cuff technology allows simultaneous segmental measurement of the brachial and ankle pressures.
Early PAD detection is vital for these reasons:
70%
of patients with PAD do not have typical symptoms and are not diagnosed
1/3
of asymptomatic patients have masked PAD
29%
of highest risk patients have PAD
13%
adult people affected globally
230 million
adult people affected globally
20 million
Americans have PAD
Why Arterial Vascular Assessment Matters
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a dominant concern for physicians and is intrinsically linked to arterial health. PAD is the occlusion of arteries due to the buildup of fatty cholesterol deposits called plaque lining the interior of arteries. As plaque formation accumulates, the arteries narrow, stiffen, and decline functionality. Plaque reduces blood flow, usually to the legs, and, if left to worsen, can lead to tissue death or even amputation. Research estimates that eight to 20 million people are affected by PAD in both the U.S. and Europe. Like many other cardiovascular diseases, over three-quarters of the population that develops Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) do not show symptoms. As a result, patients with PAD have an increased risk of stroke, heart attack, and ischemic attack. PAD patients are six times more likely to die from cardiovascular disease than healthy adults within ten years of being diagnosed.
VitalScan Plus ABI+ enables specialists to isolate issues, track problems and manage patient health using noninvasive oscillometer readings performed automatically and efficiently.
Advantages of the VitalScan Plus ABI+ System
The VitalScan Plus ABI+ system is innovative, combining PWV, PVR and 4xBP cuff-based technology for performing the ankle-brachial index (ABI) and TBI exam.
The assessment assists in the diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease (PAD). This new technology significantly improves ankle and pressure determination and PAD assessment over traditional forms of oscillometer ankle pressure estimation.
The VitalScan Plus ABI+ system offers many benefits for doctors and patients compared to the previous Doppler ultrasound method.
Early Detection and Routine Screening
Historically, ankle-brachial index (ABI) testing was performed only when Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) was suspected, due to high costs and lengthy procedures. PAD often remained undiagnosed in its early stages, as it frequently shows no symptoms. The VitalScan Plus ABI+ system introduces an innovative, rapid, and convenient way to measure ABI, enabling routine screening and early detection on a wider scale. Patients appreciate its speed, simplicity, and reliability—making routine vascular health checks more accessible.
Enhanced Accuracy & Time Efficiency
The VitalScan Plus ABI+ system is not only faster but significantly more accurate. The system simultaneously performs oscillometric blood pressure measurements on all four limbs, dramatically reducing measurement time and eliminating inaccuracies caused by blood pressure variability. This ensures precise, reliable, and highly reproducible ABI results.
Request Information
The VitalScan Plus ABI+ system is innovative, combining PWV, PVR and 4xBP cuff-based technology for performing the ankle-brachial index (ABI) and TBI exam.
The assessment assists in the diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease (PAD). This new technology significantly improves ankle and pressure determination and PAD assessment over traditional forms of oscillometer ankle pressure estimation.
The VitalScan Plus ABI+ system offers many benefits for doctors and patients compared to the previous Doppler ultrasound method.
Early Detection and Routine Screening
Historically, ankle-brachial index (ABI) testing was performed only when Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) was suspected, due to high costs and lengthy procedures. PAD often remained undiagnosed in its early stages, as it frequently shows no symptoms. The VitalScan Plus ABI+ system introduces an innovative, rapid, and convenient way to measure ABI, enabling routine screening and early detection on a wider scale. Patients appreciate its speed, simplicity, and reliability—making routine vascular health checks more accessible.
Enhanced Accuracy & Time Efficiency
The VitalScan Plus ABI+ system is not only faster but significantly more accurate. The system simultaneously performs oscillometric blood pressure measurements on all four limbs, dramatically reducing measurement time and eliminating inaccuracies caused by blood pressure variability. This ensures precise, reliable, and highly reproducible ABI results.
Request Information

The VitalScan Plus ABI+ system is a Class II medical device that is US FDA 510(K) cleared.
VitalScan Plus ABI+ testing procedure is covered by the most major insurance providers, under CPT code 93922 and 93923.
VitalScan Plus ABI+ testing procedure is covered by the most major insurance providers, under CPT code 93922 and 93923.
